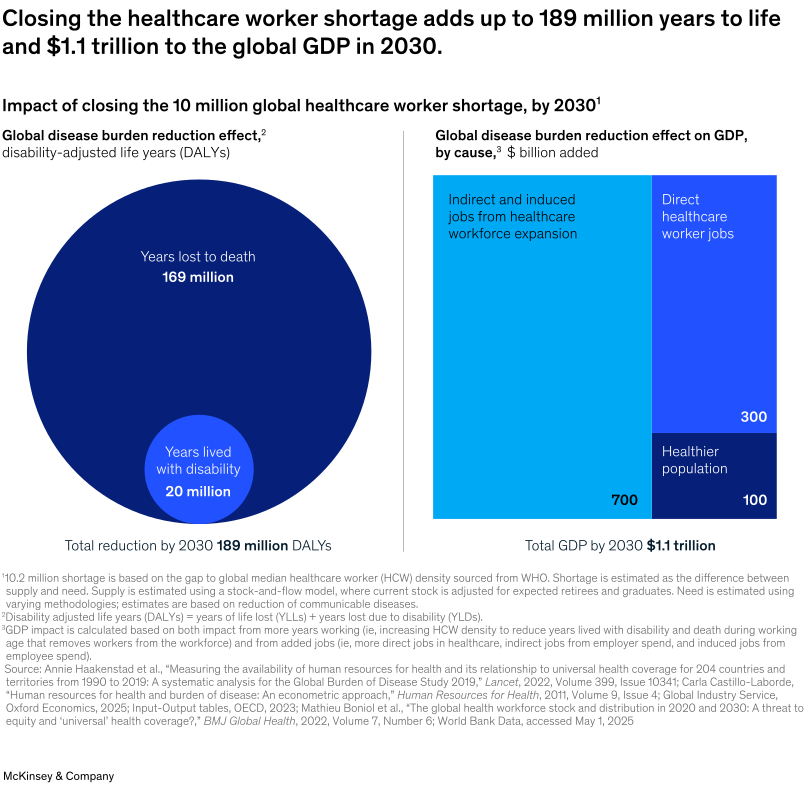
The global healthcare system stands at a crossroads. According to the McKinsey Health Institute’s latest research, at least 10 million healthcare workers will be needed by 2030 to meet growing demand—a shortage that threatens to leave 4.5 billion people without access to essential health services.
Traditional solutions focus on adding more workers: expanding medical schools, accelerating training programs, improving retention. While important, these approaches can only add about 5.6 million workers globally.
That still leaves nearly half the shortage unfilled.
The question isn’t just “How do we train more healthcare workers?” but rather “How do we fundamentally reimagine healthcare delivery to do exponentially more with existing resources?”
The Technology-Enabled Workforce Multiplier
The answer lies in virtual care technologies, particularly Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) and AI-enhanced automation. These aren’t just digital conveniences—they’re strategic workforce multipliers that address the core challenges highlighted in McKinsey’s research.
Transforming the “Who, How, and Where” of Healthcare
McKinsey’s report calls for reimagining three fundamental aspects of care delivery:
- Who Provides Care: Virtual care expands the effective reach of each healthcare professional. One physician can now monitor dozens of chronic patients continuously through connected devices and AI-powered platforms, rather than seeing them only during scheduled visits.
- How Care is Delivered: Instead of reactive, episodic care, RPM enables proactive, continuous health management. AI algorithms can detect concerning patterns in real-time, alerting providers to intervene before conditions become critical.
- Where Care is Accessed: Care delivery extends beyond hospital walls into patients’ homes and communities. This shift reduces facility burden while improving patient convenience and outcomes.
The Science Behind Virtual Care’s Impact
Research consistently demonstrates virtual care’s effectiveness as a workforce solution:
- McKinsey data shows up to 30% of nursing tasks could be automated or delegated, freeing clinicians for complex care
- JAMA research indicates remote monitoring can reduce hospital admissions by up to 38% for certain chronic conditions
- AI-enhanced clinical documentation can reduce consultation time by 26% while maintaining care quality
Each prevented hospitalization represents significant saved healthcare worker hours across emergency departments, hospital units, and specialist consultations.

AI as the Great Enabler
Artificial intelligence serves as the backbone of effective virtual care, addressing workforce shortages through:
Smart Automation
- Automated vital sign monitoring and trend analysis
- Intelligent alert systems that prioritize urgent cases
- Streamlined documentation reducing administrative burden
Clinical Decision Support
- Pattern recognition for early disease detection
- Risk stratification helping providers focus on high-need patients
- Predictive analytics preventing health crises before they occur
Workflow Optimization
- Automated patient triage and care coordination
- Integration with existing electronic health records
- Billing optimization for new care models
Prevention: The Ultimate Workforce Strategy
Perhaps the most powerful aspect of virtual care is its focus on prevention. Every diabetic crisis prevented, every heart failure episode avoided, every COPD exacerbation caught early represents:
- Fewer emergency room visits
- Reduced hospital admissions
- Less specialist intervention needed
- More healthcare workers available for unavoidable conditions
This preventive approach doesn’t just improve patient outcomes—it strategically redeploys limited healthcare resources where they’re most needed.
Real-World Implementation Models
Healthcare organizations are successfully implementing virtual care through various approaches:
- Technology-First Adoption
Organizations invest in comprehensive platforms that integrate monitoring devices, AI analytics, and care coordination tools. These systems work alongside existing workflows while dramatically expanding capacity. - Hybrid Care Models
Practices combine traditional in-person care with continuous virtual monitoring, creating a seamless care continuum that maximizes both patient engagement and provider efficiency. - Collaborative Care Networks
Healthcare systems partner with virtual care specialists to extend their reach, sharing expertise and resources across geographic boundaries.
The Economic Case for Virtual Care
The numbers are compelling:
- CMS has significantly increased reimbursement rates for RPM and chronic care management services
- 76% of patients prefer remote monitoring options when available
- Early adopters report substantial improvements in both clinical and financial outcomes
These aren’t just pilot programs—they represent a fundamental shift in how healthcare economics work, making prevention financially sustainable.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Successful virtual care deployment requires addressing common barriers:
- Technology Integration
Modern platforms must seamlessly integrate with existing systems rather than disrupting established workflows. The best solutions become invisible to providers, enhancing rather than complicating their daily routines. - Patient Engagement
Effective virtual care platforms prioritize user experience, making it easy for patients to participate actively in their health management without requiring technical expertise. - Regulatory Compliance
Solutions must meet all CMS requirements for documentation and billing while minimizing administrative burden on healthcare teams.
Case Study: Comprehensive Virtual Care Platforms
Companies like MEDOMENT exemplify how comprehensive virtual care platforms address workforce shortages. Their approach combines:
- Intuitive technology that adapts to existing practice workflows
- AI-enhanced intelligence that complements human clinical expertise
- Flexible implementation options from DIY platforms to fully managed services
- Revenue-positive models that make adoption financially attractive
Such platforms demonstrate how virtual care can deliver the “triple win”: better patient outcomes, increased provider efficiency, and reduced system costs.
The Path Forward
The healthcare workforce shortage represents both a crisis and an opportunity. While we continue efforts to train and retain more healthcare workers, virtual care technologies offer an immediate path to multiply the impact of existing resources.
Success requires:
- Strategic adoption of proven virtual care technologies
- Integration with existing workflows rather than wholesale replacement
- Focus on prevention to reduce downstream demand
- Patient-centered design that improves rather than complicates the care experience
Looking Ahead
The future of healthcare won’t be defined by choosing between human care and technology—it will be characterized by their seamless integration. Virtual care platforms, powered by AI and focused on prevention, enable healthcare workers to practice at the top of their license while extending their reach exponentially.
As McKinsey’s research makes clear, solving the healthcare workforce shortage requires more than traditional approaches. It demands a fundamental reimagining of care delivery—one where technology amplifies human expertise rather than replacing it.
The transformation is already underway. Healthcare organizations that embrace comprehensive virtual care solutions today will be best positioned to meet tomorrow’s challenges while delivering exceptional care to more patients than ever before.



